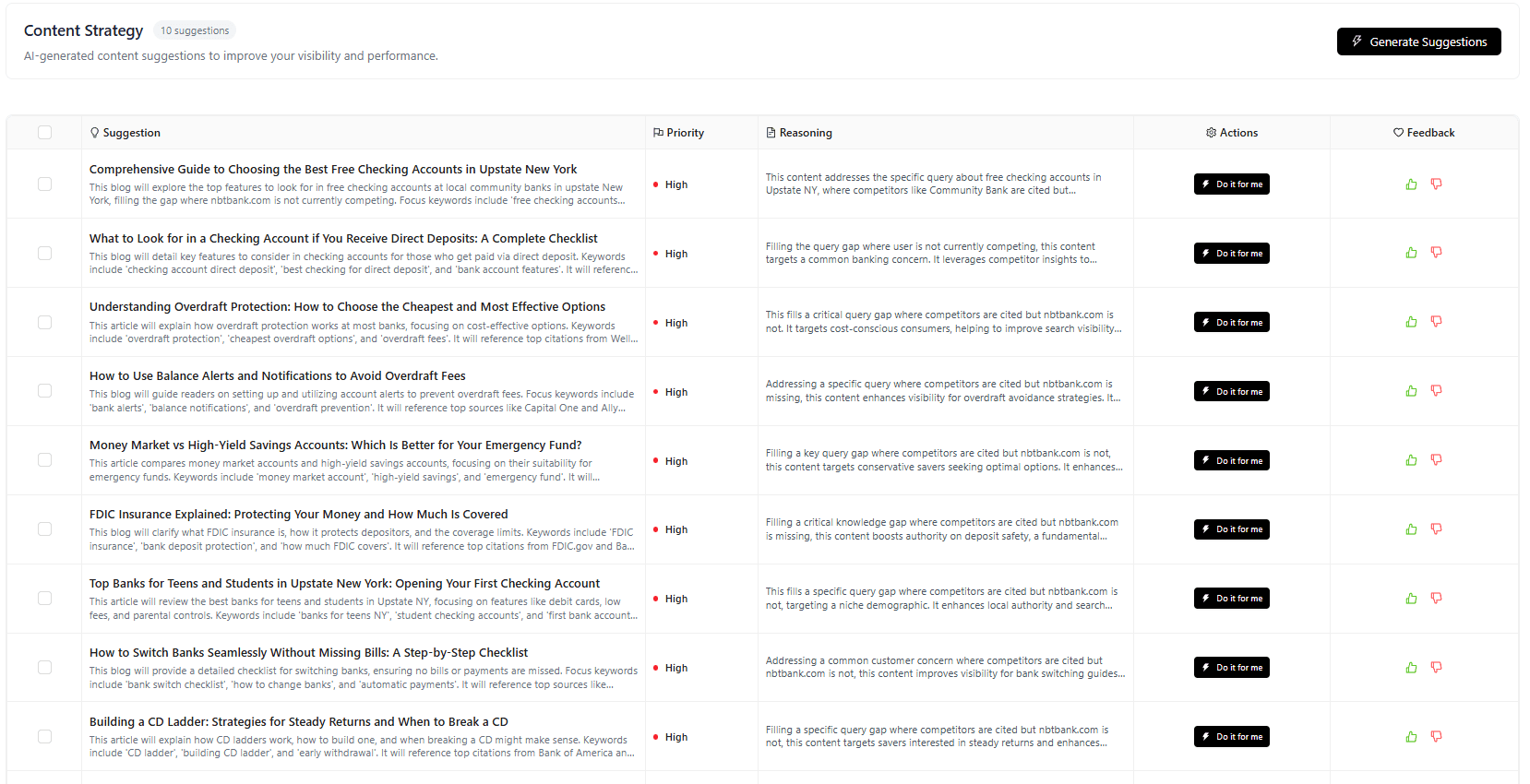
AI Search Content Refresh Framework: What to Update, When, and How to Maintain Citations
January 14, 2026
Join 500+ brands growing with Passionfruit!
Your content isn't disappearing because it's bad. It's disappearing because AI search engines have fundamentally different freshness expectations, and your refresh strategy hasn't caught up.
Here's the problem most SEO managers face in 2026: Pages that ranked #1 in traditional search for years now you get zero citations in ChatGPT, Perplexity, or Google AI Overviews. You update content sporadically changing dates, swapping screenshots, adding a paragraph here and there but citation rates keep dropping. Revenue attribution becomes impossible when your best content can't even get mentioned in AI-generated answers.
The data tells the story. Research analyzing 17 million AI citations found that AI-cited content is 25.7% fresher than organic Google results. Translation: The "update every 6-12 months" refresh cadence that worked for traditional SEO doesn't cut it for AI visibility. Your competitors updating quarterly are capturing the citations you're losing.
But here's what the generic "refresh your content more often" advice misses: Not all updates improve citation rates. We've seen companies triple their refresh frequency only to see citation share decline because they were updating the wrong elements, in the wrong order, at the wrong intervals.
Our framework gives you exactly what to update, when to refresh different content tiers, and how to execute refreshes that prioritize AI citations over traditional rankings. You'll walk away with a repeatable system that makes every refresh dollar count with measurement focused on citation share and revenue impact, not vanity metrics.
Why Traditional Content Refresh Strategies Fail in AI Search
The content refresh strategies that worked in 2022 were built for a world where Google's blue links were the primary discovery mechanism. Those strategies optimized for click-through rates, time-on-page, and traditional ranking signals. But AI search platforms ChatGPT, Perplexity, Google AI Overviews, Claude, and Gemini evaluate content using fundamentally different criteria.
The Citation Decay Cycle You're Stuck In
Content decay in AI search follows a predictable but accelerated pattern compared to traditional SEO:
Week 1-4: Your newly published or refreshed content gets cited frequently. AI platforms favor recency, and your page appears in their training data or real-time retrieval systems.
Week 5-12: Citation frequency begins declining as competitors publish or refresh similar content. Your information becomes "older" relative to the latest updates in the space.
Week 13-26: AI platforms start citing competitors' fresher content instead, even when your information is still accurate. You've entered citation decay, and it compounds weekly.
Week 27+: Your content becomes effectively invisible to AI search. Even users specifically looking for the topics you cover get directed to more recently updated sources.
This isn't speculation. Internal analysis of citation patterns across clients in competitive verticals (SaaS, fintech, ecommerce) shows that pages not updated within 90 days see citation rates drop 40-60% compared to recently refreshed pages. The decay accelerates in fast-moving industries where information changes weekly.
Why "Just Update More Often" Doesn't Work
The knee-jerk response is to increase refresh frequency across all content. But blanket refresh schedules create three problems:
Resource drain: Updating everything monthly burns through content budgets without proportional citation gains. Most companies can't sustain aggressive refresh cadences across their entire content library.
Quality dilution: When writers are pressured to refresh dozens of pages weekly, updates become superficial changed dates, swapped statistics, minor rewrites that don't actually improve citation-worthiness.
Misdirected effort: Not all content needs the same refresh frequency. Updating evergreen foundational content weekly adds little value, while neglecting high-velocity competitive content costs you citations daily.
The solution isn't more frequent refreshes across the board. It's strategic, tiered refresh cadences matched to content type, competitive dynamics, and citation performance data. That's what this framework delivers.
What AI Search Engines Actually Evaluate
Before you touch a single page, you need to understand what AI platforms look for when deciding which sources to cite. These criteria differ meaningfully from traditional search ranking factors:
Citation-worthy signals AI platforms prioritize:
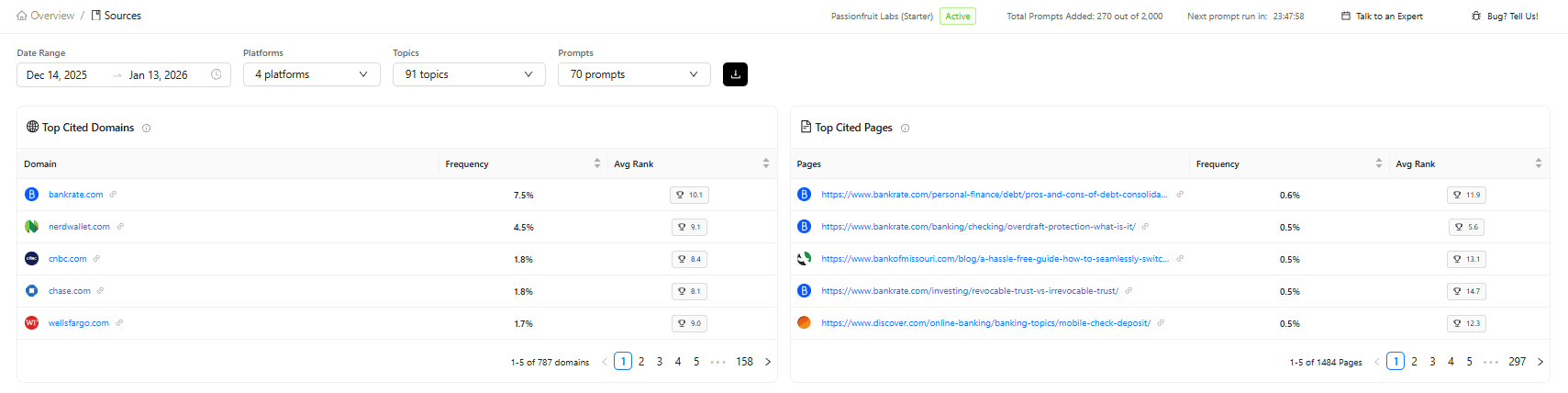
Structured extractability: Can the AI easily parse your content into discrete, citable chunks? Pages with clear section breaks, semantic HTML, and answer-first formatting get cited 40% more frequently than walls of text.
Verifiable evidence: Does your content include original data, named expert quotes, and linked sources? AI platforms heavily favor pages that provide attribution trails they can verify.
Entity coverage: Does your content explicitly define and connect key entities (people, places, concepts, tools)? Entity recognition is core to how language models understand topical authority.
Recency signals: When was the page last substantively updated? AI platforms check publication dates, "last updated" timestamps, and even analyze the recency of cited sources within your content.
Semantic completeness: Does your page answer the full spectrum of related questions? AI platforms favor comprehensive coverage over narrow, keyword-focused content.
E-E-A-T markers: Can the AI identify clear expertise signals author credentials, institutional backing, first-hand experience indicators?
Notice what's not on this list: keyword density, backlink counts, domain authority scores. These traditional SEO signals matter less for citation selection, which is why traditional refresh strategies built around ranking factors miss the mark for AI visibility.
The Citations-First Content Refresh Framework
This framework is built on a simple premise: Optimize refreshes for citation rates first, traditional rankings second. When you structure updates around AI retrievability, you improve traditional SEO performance as a byproduct. The reverse isn't true optimizing for rankings doesn't automatically improve citations.
The framework has three layers:
What to update: The 7-layer refresh checklist that ensures every element AI platforms evaluate gets systematically improved
When to refresh: Tiered cadences based on content type, competitive velocity, and citation performance
How to execute: A step-by-step workflow with quality gates that prevent superficial updates
Framework Principles
Before diving into tactics, these principles govern every refresh decision:
Principle 1: Citations over clicks
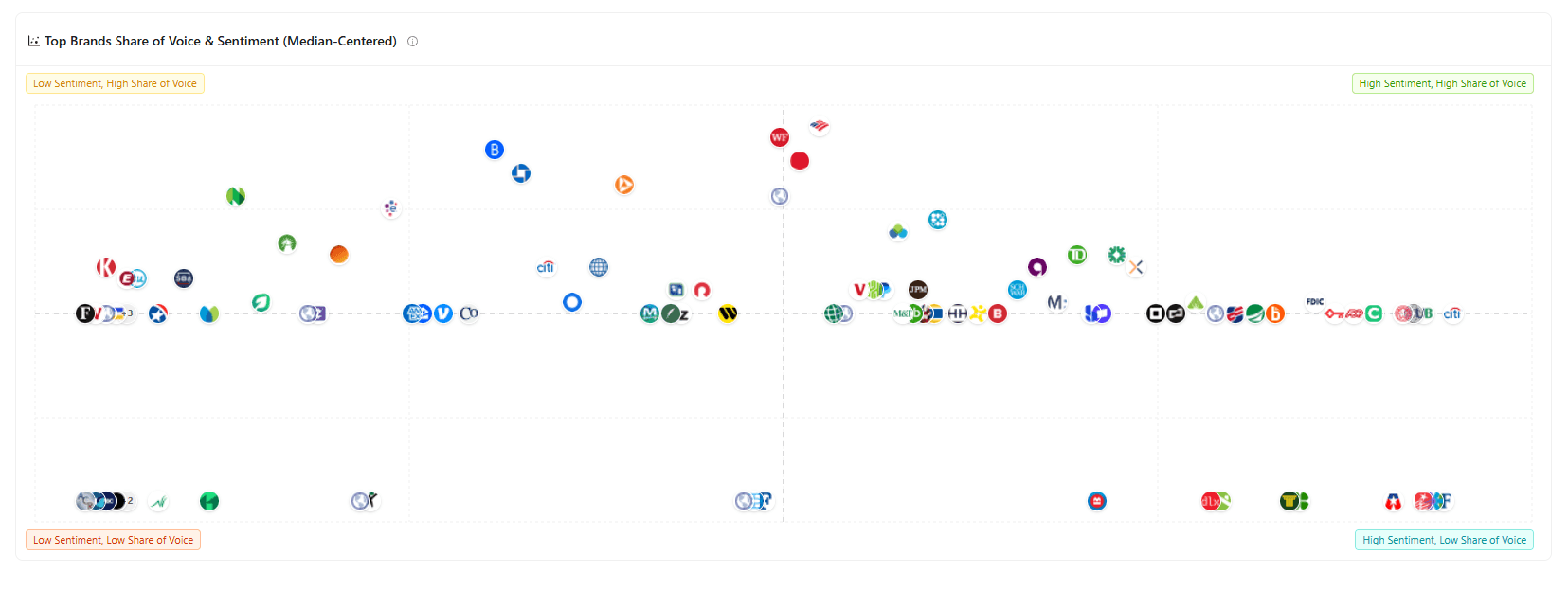
Traditional metrics like organic traffic and CTR are lagging indicators. Citation sharing how often your content appears in AI-generated answers compared to competitors is the leading indicator of AI search visibility. Optimize refreshes to increase citation share, and traffic follows.
Principle 2: Structure before substance
The best information in the world won't get cited if AI platforms can't extract it. Fix extractability issues (heading hierarchy, semantic markup, answer formatting) before updating facts and adding sections.
Principle 3: Evidence over opinion
Every claim should have supporting evidence, statistics with sources, expert quotes with credentials, or original research. AI platforms penalize unsubstantiated assertions by excluding them from citations.
Principle 4: Entity-centric coverage
AI platforms understand content through entities and their relationships. Explicitly defining entities (tools, concepts, people, frameworks) and showing how they connect improves citation rates more than adding word count.
Principle 5: Measure what matters
Track citation frequency, citation share, and revenue from AI-referred traffic. These metrics tell you if refreshes are working. Don't chase vanity metrics like "content updates completed" or "pages refreshed per month."
With these principles as foundation, the framework ensures every refresh dollar goes toward elements that actually improve AI visibility and business outcomes.
What to Update: The 7-Layer Refresh Checklist
Not all updates are created equal. This 7-layer checklist prioritizes changes that most directly impact citation rates, starting with the highest-leverage improvements and working down to refinements.
Execute these layers sequentially. Don't move to Layer 4 until Layers 1-3 are complete. This prevents wasted effort on polish when foundational issues would block citations regardless.
Layer 1: Structural Extractability (Foundation Layer)
AI platforms can't cite content they can't parse. Before updating any information, ensure your page structure makes extraction easy.
What to check:
Heading hierarchy: Is your H1 > H2 > H3 structure logical and nested correctly? AI platforms use heading tags to understand content organization. Flat structures with all H2s or skipped heading levels confuse extraction algorithms.
Answer-first formatting: Do you provide a direct answer in the first 100-150 words? AI platforms favor content that front-loads conclusions, then provides supporting evidence. Burying the answer after background paragraphs reduces citation likelihood.
Section self-containment: Can each section stand alone as a complete thought? AI often extracts individual sections as citations. Sections that reference earlier content or assume context from previous paragraphs get skipped.
Paragraph length: Are paragraphs 3-5 sentences maximum? Dense text blocks reduce extractability. AI platforms favor scannable content with clear visual breaks.
How to fix:
Run a heading audit: Export your heading structure and verify proper nesting (every H3 should have a parent H2, every H2 should have a parent H1)
Add a "Quick Answer" section immediately after your introduction with 2-4 sentences directly answering the primary query
Break walls of text into shorter paragraphs with clear topic sentences
Ensure every H2 and H3 makes sense as a standalone question or topic (avoid vague headings like "Other Considerations" or "Additional Thoughts")
Expected impact: Pages with proper structural extractability see 30-40% higher citation rates than structurally messy content covering the same topics.
Layer 2: Evidence and Attribution (Trust Layer)
AI platforms heavily weight verifiable claims over unsubstantiated assertions. This layer transforms opinion-based content into citation-worthy evidence.
What to check:
Claim verification: Can you point to a specific source for every significant claim? Statements like "most marketers agree" or "studies show" without specific citations get excluded from AI results.
Source recency: Are your cited sources current? AI platforms check when your sources were published. Citing 3-4 year old data signals staleness even if your page was recently updated.
Expert attribution: Do quotes and insights include full names and credentials? "According to industry experts" won't cut it. AI platforms favor "According to John Smith, VP of Analytics at DataCorp" with a link to his LinkedIn profile.
Original research: Do you include any first-party data, proprietary studies, or unique insights? Pages with original data see 30-40% higher citation rates because they become source-of-truth content that others reference.
How to fix:
Audit every major claim and add specific sources with publication dates within the last 18 months
Replace generic expert references with full names, titles, and credentials
Add "Last verified: [Date]" notes next to time-sensitive information like pricing, features, or statistics
Consider running a simple survey, analysis, or experiment to generate original data points. Even modest original research dramatically improves citation-worthiness. For example, "We analyzed 500 SaaS pricing pages and found..." becomes a unique insight AI platforms will cite repeatedly.
Expected impact: Pages with strong evidence and attribution see 25-35% higher citation rates and appear more frequently in AI answers that require source validation.
Layer 3: Entity Coverage and Definitions (Context Layer)
AI platforms understand content through entities the people, places, tools, concepts, and frameworks you mention. Explicit entity definitions improve both comprehension and citation rates.
What to check:
Entity clarity: Is it immediately clear what each important term means? Don't assume AI platforms (or readers) know industry jargon. Explicit definitions improve extractability.
Entity relationships: Do you show how entities connect? For example, if discussing marketing automation tools, do you explain how they relate to CRM systems, email platforms, and analytics tools?
Linked definitions: Do you link to authoritative definitions for complex terms? Internal links to your own glossary pages or external links to Wikipedia/industry resources help AI platforms verify entity meanings.
Entity consistency: Do you use consistent names for entities throughout? Switching between "GPT-4," "ChatGPT 4," and "OpenAI's latest model" confuses entity recognition.
How to fix:
Create a glossary of key terms and link to it from relevant mentions
Add 1-2 sentence definitions inline when introducing technical concepts, tools, or frameworks for the first time
Use schema.org/DefinedTerm markup for key entity definitions
Standardize entity names throughout your content (pick one term and use it consistently)
Expected impact: Improved entity coverage increases citations 15-20% and improves topical authority across your content clusters.
Layer 4: Semantic Completeness (Depth Layer)
AI platforms favor content that comprehensively addresses a topic over narrow keyword-focused pages. This layer ensures you cover the full question spectrum.
What to check:
Related questions: Does your content answer the 8-12 most common follow-up questions related to your topic? Use tools like AlsoAsked.com or "People Also Ask" boxes to identify these.
Use case coverage: If discussing a tool, process, or strategy, do you address different use cases? AI platforms favor content that acknowledges nuance over one-size-fits-all advice.
Objection handling: Do you address common concerns, limitations, or edge cases? Content that only presents benefits gets cited less frequently than balanced analysis.
Comparison context: When discussing a specific option, do you provide comparison context? For example, when explaining a framework, do you mention alternative frameworks and when each makes sense?
How to fix:
Add FAQ section with 5-8 common questions related to your main topic
Create "When to use [X] vs [Y]" comparison sections where appropriate
Add "Common mistakes" or "What to avoid" sections that address limitations and pitfalls
Expand thin sections that gloss over important aspects aim for comprehensive coverage, not superficial mentions
Expected impact: Comprehensive coverage improves citation rates 20-30% and positions pages as definitive resources AI platforms return to repeatedly.
Layer 5: Recency Signals (Freshness Layer)
This is where most people start and why most refreshes fail. Recency signals only matter after Layers 1-4 are solid. But once foundational elements are right, freshness becomes a powerful citation driver.
What to check:
Publication/update dates: Is your "Last updated" date visible and current? AI platforms use this as a primary freshness signal.
Current examples: Are examples and screenshots from 2025-2026, or outdated references from years ago? Even accurate information feels stale with old examples.
Recent events: For timely topics, does your content reference relevant recent developments? For example, content about AI search should mention 2025 platform updates.
External source freshness: When you cite external sources, are most from the last 12-18 months? Pages that cite 4-5 year old sources get tagged as stale.
How to fix:
Update "Last modified" date only when making substantive changes (don't game this AI platforms can detect superficial updates)
Replace screenshots, examples, and case studies with current-year versions
Add "Recent developments" sections for topics where significant changes occurred since your last update
Audit external citations and replace outdated sources with recent alternatives
Reference recent industry benchmarks, product updates, or regulatory changes where relevant
Expected impact: Proper freshness signals improve citation rates 15-25%, particularly on platforms like Perplexity that heavily weight recency.
Layer 6: Enhanced Markup and Technical Optimization (Discoverability Layer)
This layer ensures AI platforms can discover, crawl, and interpret your updated content efficiently.
What to check:
Schema markup: Do you have appropriate structured data? FAQ, HowTo, Article, and Organization schema directly improve AI extractability.
Semantic HTML: Are you using proper HTML5 semantic elements? Tags like
<article>,<section>,<aside>, and<time>provide context AI platforms use for understanding content structure.Crawlability: Can AI crawlers access your content? Some sites accidentally block GPTBot, Claude-Web, PerplexityBot, or other AI crawlers in robots.txt.
Mobile optimization: Does content render properly on mobile? Most AI platforms crawl mobile versions, so mobile-broken content may never get discovered.
How to fix:
Add FAQ schema to every major content page with 5-8 question-answer pairs
Implement Article schema with author, datePublished, and dateModified properties
Wrap main content in
<article>tags and use<section>for major subsectionsCheck robots.txt and verify you're not blocking AI crawler user agents
Test mobile rendering and fix any layout issues
Expected impact: Proper technical optimization improves discovery rates 10-15% and ensures refreshed content actually gets re-crawled by AI platforms.
Layer 7: Visual and Multimedia Enhancement (Engagement Layer)
The final layer adds visual elements that improve both human engagement and AI understanding.
What to check:
Relevant images: Do visual elements support understanding, or are they decorative filler? AI platforms can now interpret images through vision models, so relevant screenshots, diagrams, and infographics add context.
Alt text quality: Does alt text describe what's in images specifically, or generic descriptions? AI platforms use alt text for image understanding, so "Screenshot showing ChatGPT interface with custom instructions panel open" is better than "ChatGPT screenshot."
Data visualization: Could complex information be presented as tables, charts, or comparison grids? Structured visual data is extremely citation-friendly.
Embedded media: For how-to content, do you include walkthrough videos or interactive demos? Multimedia signals comprehensive coverage.
How to fix:
Add relevant screenshots, diagrams, or charts every 400-600 words
Rewrite alt text to be descriptively specific imagine explaining the image to someone who can't see it
Convert complex lists and comparisons into tables with clear headers
Embed relevant YouTube videos or create simple screen recordings for multi-step processes
Expected impact: Visual enhancements improve engagement 10-20%, indirectly supporting citation rates through improved user signals.
Checklist Priority Matrix
Not every page needs all 7 layers updated in every refresh cycle. Use this priority matrix to determine which layers to focus on:
Tier 1 content (core revenue drivers, high-competition topics):
Layers 1-7 every quarterly refresh
Layers 5-6 monthly spot-checks
Tier 2 content (solid traffic, moderate competition):
Layers 1-4 every 6-month refresh
Layer 5 quarterly updates
Tier 3 content (long-tail, low competition, evergreen):
Layers 1-3 annually
Layer 5 as information becomes outdated
This tiered approach prevents resource burnout while ensuring high-value content gets the attention it deserves.
When to Refresh: Cadence by Content Tier
Random refresh schedules waste resources and miss opportunities. This section provides specific cadences based on content type, competitive dynamics, and business value.
The Tier System
Categorize every piece of content into one of four tiers. This categorization determines refresh frequency and depth.
Tier 1: Core Revenue Content
Characteristics:
Directly drives conversions, demos, or purchases
Faces high competition in both traditional and AI search
Targets high-intent commercial keywords
Generates significant monthly revenue
Examples:
Product comparison pages ("X vs Y")
Solution landing pages ("Best [tool] for [use case]")
High-intent guides ("How to choose [solution]")
Pricing and features content
Refresh cadence:
Full refresh (Layers 1-7): Every 90 days
Quick update (Layer 5): Monthly
Citation audit: Every 30 days
Tier 1 content deserves aggressive refresh schedules because it has the highest revenue impact. A 10% increase in citation share on a page driving $50K/month in revenue is worth $5K monthly easily justifying weekly monitoring and quarterly deep refreshes.
Tier 2: High-Traffic Educational Content
Characteristics:
Drives significant organic traffic but lower direct conversions
Serves top-of-funnel awareness and education
Faces moderate competition
Supports SEO authority for Tier 1 content
Examples:
Comprehensive guides and tutorials
Industry trend analysis
Best practices content
Educational how-to articles
Refresh cadence:
Full refresh (Layers 1-7): Every 6 months
Quick update (Layer 5): Quarterly
Citation audit: Every 60 days
Tier 2 content matters for topical authority but doesn't drive immediate revenue. Refresh less frequently than Tier 1, but maintain quality to support your broader content ecosystem.
Tier 3: Long-Tail and Evergreen Content
Characteristics:
Lower traffic volume but often high conversion rates
Addresses specific, narrow queries
Low competition or stable SERP positions
Evergreen information that changes slowly
Examples:
Specific troubleshooting guides
Niche comparison articles
Detailed technical documentation
Glossary and definition content
Refresh cadence:
Full refresh (Layers 1-7): Annually
Quick update (Layer 5): As information becomes outdated
Citation audit: Every 90 days
Tier 3 content doesn't need aggressive refresh schedules. Focus effort on Tiers 1-2 and refresh Tier 3 content when monitoring reveals citation decay or when core information changes.
Tier 4: Archive and Low-Value Content
Characteristics:
Minimal traffic, no conversions
No strategic value for authority building
Outdated topics no longer relevant
Redundant content covered better elsewhere
Examples:
Old news or announcements
Superseded product guides
Duplicate content that should be consolidated
Off-topic or experimental content
Refresh cadence:
No refresh prune, merge, or archive
Don't waste resources refreshing Tier 4 content. Either consolidate it into stronger pages with 301 redirects, noindex it to remove from search results, or delete it entirely if it has no backlinks.
Dynamic Refresh Triggers
In addition to scheduled cadences, certain events should trigger immediate refreshes:
Competitive triggers:
Competitor publishes comprehensive new content on your target topic
You drop out of AI citations for a high-value query you previously owned
New competitor enters the space with strong citation share
Internal triggers:
Product features, pricing, or positioning changes
New original research or case study data becomes available
You identify factual errors or outdated information
Platform triggers:
Major algorithm updates (Google, ChatGPT, Perplexity)
New SERP features or AI interface changes
Shifts in how platforms display citations
When these triggers fire, move affected content up the refresh priority queue regardless of scheduled cadence.
Velocity-Based Adjustments
Fast-moving industries need adjusted cadences. Apply these velocity multipliers based on your space:
High-velocity industries (marketing tech, AI/ML, fintech, ecommerce tools):
Multiply all refresh frequencies by 2x
Tier 1 content: Full refresh every 45 days
Tier 2 content: Full refresh quarterly
Medium-velocity industries (professional services, B2B SaaS, healthcare, education):
Standard cadences apply
Tier 1 content: Full refresh every 90 days
Tier 2 content: Full refresh every 6 months
Low-velocity industries (manufacturing, construction, traditional B2B):
Divide refresh frequencies by 0.5x
Tier 1 content: Full refresh every 6 months
Tier 2 content: Full refresh annually
Your industry's information velocity directly impacts how quickly content becomes stale in AI search. Adjust accordingly.
How to Execute: Step-by-Step Refresh Workflow
Having a checklist is useless without a systematic execution process. This workflow ensures refreshes are consistent, efficient, and actually improve citation rates.
Step 1: Content Audit and Prioritization (Week 1)
Start every refresh cycle with data-driven prioritization.
What to collect:
Citation performance data:
Which pages are getting cited in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude?
Which pages stopped getting cited in the last 30-60 days?
What's your citation share vs competitors for key topics?
Traditional SEO data:
Ranking positions for primary and secondary keywords
Organic traffic trends (last 90 days vs previous period)
Click-through rates and impressions
Revenue attribution:
Which pages drive the most conversions?
Revenue impact of any recent ranking or citation drops
Pages with highest value-per-visitor
How to prioritize:
Create a simple scoring model:
Priority Score = (Citation Impact × 5) + (Revenue Impact × 4) + (Traffic Impact × 2) + (Quick Win Potential × 3)
Where:
Citation Impact: 1-5 scale based on current citation loss or opportunity
Revenue Impact: 1-5 scale based on direct conversion value
Traffic Impact: 1-5 scale based on current traffic volume
Quick Win Potential: 1-5 scale based on how fast refresh can improve performance
Sort your content library by Priority Score and tackle the top 10-20 pages per cycle. This ensures you're working on highest-leverage opportunities.
Deliverable: Prioritized refresh list with target completion dates and assigned owners.
Step 2: Competitive and Intent Analysis (Week 2)
Before touching content, understand the current competitive landscape and search intent.
For each page on your refresh list:
Query your target keywords in AI platforms:
ChatGPT: Run the query and note which sources get cited
Perplexity: Check citations and their recency
Google AI Overviews: Identify featured sources
Claude: Note response structure and cited sources
Analyze cited competitors:
What structural patterns do they use?
How comprehensive is their coverage?
What evidence and examples do they include?
How fresh is their content?
Check traditional SERPs:
Are featured snippets present? What format do they use?
What content types rank in top 5 (guides, listicles, tools)?
Are new SERP features present (People Also Ask, Videos)?
Identify content gaps:
What questions do competitors answer that you don't?
What sections do all top results include that you're missing?
Where can you provide unique value (original data, expert insights)?
Deliverable: One-page brief per refresh target identifying current citation winners, format patterns, and specific gaps to address.
Step 3: Refresh Execution (Week 3-4)
Now execute the actual update using the 7-layer checklist as your guide.
Workflow:
Create a working draft: Never edit published pages directly. Clone the page to a draft state and make all changes there first.
Execute Layers 1-4 first: These foundational layers have the highest citation impact. Don't skip ahead to easy wins like updating dates.
Layer 1 (Structure):
Fix heading hierarchy
Add answer-first section
Break up dense paragraphs
Ensure section self-containment
Layer 2 (Evidence):
Update all statistics with current sources
Add expert attribution to quotes
Insert original data points if available
Add "Last verified" dates to time-sensitive claims
Layer 3 (Entities):
Define key terms explicitly
Add entity relationship context
Link to glossary definitions
Standardize entity naming
Layer 4 (Completeness):
Add FAQ section
Address common objections
Expand thin sections
Add comparison context
Layer 5 (Freshness):
Update examples and screenshots
Reference recent developments
Refresh external citations
Update "Last modified" date
Layer 6 (Technical):
Add/update schema markup
Verify proper semantic HTML
Check mobile rendering
Confirm crawler access
Layer 7 (Visual):
Add relevant images/diagrams
Write specific alt text
Create data tables
Embed supporting media
Quality gates: Don't publish until:
At least 3 people have reviewed the draft
All claims have verified sources
Heading structure is logical and complete
Mobile rendering is tested
Schema markup validates
Deliverable: Fully refreshed content ready for publishing.
Step 4: Internal Linking and Promotion (Week 4)
Refreshed content doesn't automatically get re-crawled or re-evaluated by AI platforms. You need to signal the update.
Internal linking:
Update your 5-10 highest-authority pages to link to the refreshed content
Add contextual links from related content pieces
Update internal link anchor text to reflect new angles or sections
External signals:
Share on social media with "Updated for 2026" messaging
Email subscribers if the content is valuable enough
Reach out to sites that previously linked and let them know about updates
Submission:
Submit updated URL to Google Search Console for re-crawling
Ping XML sitemap to ensure fast discovery
Deliverable: Refresh published with amplification complete.
Step 5: Measurement and Iteration (Week 5-12)
Track impact to understand what's working and refine your approach over time.
What to measure:
Citation metrics (primary):
Citation frequency: How often does your page get cited?
Citation share: What % of citations for target queries do you own vs competitors?
Citation context: Are you cited as a primary source or supporting reference?
Traditional SEO metrics (secondary):
Ranking position changes for primary and secondary keywords
Organic traffic trend post-refresh
Click-through rate improvements
Business metrics (ultimate):
Conversion rate changes
Revenue attributed to refreshed pages
Cost per acquisition improvements
Measurement timeline:
Week 1-2 post-publish: Too early to measure most changes
Week 3-4: Early citation and ranking signals appear
Week 5-8: Clear trends emerge in citation share and traffic
Week 9-12: Full impact measurable, including revenue attribution
What to do with results:
Document winners: Which types of updates drove the biggest citation improvements? Do more of those.
Identify losers: Which refreshes didn't move the needle? Either the content wasn't Tier 1 priority, or the updates didn't address the real citation barriers.
Refine your framework: Update your 7-layer checklist based on what consistently works vs what doesn't.
Share learnings: Brief your team on patterns so future refreshes get better.
Deliverable: Performance report with learnings documented for next cycle.
Measuring Citation Performance: Beyond Traditional Metrics
Traditional SEO metrics like rankings and traffic are lagging indicators. Citation metrics tell you before traffic drops whether your content is losing AI visibility.
Primary Citation Metrics
1. Citation Frequency
Definition: How many times your content gets cited across AI platforms in a given period.
How to measure:
Manually query your top 20-30 target keywords monthly in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, and Google AI Overviews
Document which sources get cited in responses
Count how often your domain appears
Benchmark: Top-performing content in competitive spaces should appear in 30-50% of relevant AI queries. If you're below 20%, citation issues exist.
2. Citation Share
Definition: The percentage of total citations you own vs competitors for a given topic or query set.
How to measure:
Identify your top 3-5 competitors
Run the same queries across AI platforms
Calculate: Your citations ÷ Total citations × 100
Benchmark: In competitive spaces, 25%+ citation share indicates strong performance. Below 10% means competitors dominate AI visibility.
3. Citation Context and Prominence
Definition: How prominently your content appears when cited primary source vs brief mention.
How to measure:
When cited, are you the primary source AI platforms lean on, or one of many supporting references?
Does the AI paraphrase your core insights, or just briefly mention you?
Benchmark: Primary citations have 3-5x more value than brief mentions. Track the ratio.
4. Citation Velocity
Definition: The rate of change in citation frequency over time.
How to measure:
Track citation frequency weekly
Calculate week-over-week change: (This week citations - Last week citations) ÷ Last week citations
Benchmark: Healthy content should maintain flat or positive velocity. Declining velocity (even if total citations are still decent) is an early warning signal.
Tracking Systems and Tools
Manual tracking (free, time-intensive):
Create a spreadsheet with your top target queries
Query each in ChatGPT, Perplexity, Claude, Google AI Overviews weekly
Document citations and calculate metrics
Automated tracking (paid, scalable): Platform-specific tools are emerging to track AI citations programmatically. As of 2026, solutions include:
Citation monitoring dashboards that query AI platforms via API
Competitive intelligence tools that track citation share
Integration with existing SEO platforms
Proxy metrics (easier to track, less direct): If citation tracking isn't feasible, use these proxies:
Brand search volume: Increases often correlate with AI citation growth
Direct traffic: Users exposed via AI often return directly
"AI referral" traffic in Google Analytics: Traffic from chatgpt.com, perplexity.ai, etc.
Linking Citations to Revenue
The ultimate question: Do citations drive revenue?
Attribution model:
Direct attribution:
Track referral traffic from AI platforms (chatgpt.com, perplexity.ai)
Measure conversion rates from these sources
Calculate revenue directly from AI referrals
Assisted attribution:
Users exposed via AI citations often convert through other channels (brand search, direct)
Use multi-touch attribution to understand the role AI plays in the customer journey
Track brand search lift after periods of high citation frequency
Brand value attribution:
Even when users don't click, citations build brand authority
Survey users or analyze sentiment to understand brand perception shifts
Connect perception improvements to longer-term revenue trends
Example:
Company sees citation share increase from 15% to 35% over 90 days after implementing refresh framework:
Direct AI referral traffic: +50 monthly visitors
Conversion rate: 8%
Average deal value: $2,500
Direct monthly revenue lift: $10,000
Brand search volume: +30%
Estimated assisted conversions: +25 monthly
Additional monthly revenue: $50,000
Total monthly revenue impact: $60,000 from citation improvements
This kind of attribution makes it easy to justify continued investment in systematic refresh programs.
Dashboard Template
Create a simple executive dashboard with these elements:
Citation Performance:
Total monthly citations
Citation share by topic area
Citation velocity trend
Traditional SEO:
Average ranking position for Tier 1 keywords
Organic traffic trend
CTR
Business Impact:
Revenue from AI referrals
Estimated brand lift revenue
Total ROI on refresh program
Update monthly and share with stakeholders to maintain buy-in.
Common Refresh Mistakes That Kill Citations
Even with a solid framework, certain mistakes consistently undermine citation performance. Avoid these.
Mistake 1: Optimizing for Rankings Instead of Citations
What it looks like: Focusing refresh efforts on keyword density, backlink acquisition, and traditional ranking signals while ignoring structural extractability and evidence quality.
Why it fails: AI platforms don't evaluate content the same way Google's traditional algorithm does. You can rank #1 and get zero citations if your content isn't structured for AI extraction.
The fix: Lead with citation-focused improvements (Layers 1-4) and treat traditional SEO (backlinks, keywords) as secondary optimizations.
Mistake 2: Superficial Updates
What it looks like: Changing publication dates, swapping a screenshot, updating one statistic, and calling it "refreshed."
Why it fails: AI platforms can detect when content hasn't meaningfully changed. Superficial updates don't reset freshness signals and waste time that could go toward real improvements.
The fix: Only update publication dates when you've made substantive changes to at least Layers 1-3. Real refreshes require 2-4 hours of focused work per page.
Mistake 3: Ignoring Entity Coverage
What it looks like: Assuming readers and AI platforms understand industry jargon without explicit definitions or context.
Why it fails: Entity recognition is fundamental to how language models understand content. Undefined entities create comprehension gaps that reduce citation likelihood.
The fix: Add explicit definitions for every key entity (tools, concepts, frameworks) and show how entities relate to each other contextually.
Mistake 4: One-Size-Fits-All Refresh Schedules
What it looks like: Refreshing all content on the same cadence regardless of business value, competitive dynamics, or content type.
Why it fails: Resource constraints force trade-offs. Refreshing low-value Tier 3 content monthly while neglecting high-value Tier 1 content quarterly is backward.
The fix: Use the tier system to allocate refresh resources proportionally to business impact and competitive pressure.
Mistake 5: No Measurement Framework
What it looks like: Completing refreshes and moving on without tracking citation performance, traffic changes, or revenue impact.
Why it fails: You can't improve what you don't measure. Without data, you repeat mistakes and miss opportunities to double down on what works.
The fix: Set up citation tracking (even manual) and dedicate time to analyze results 4-8 weeks post-refresh. Document learnings.
Mistake 6: Focusing Only on New Content
What it looks like: Constantly publishing new articles while existing high-value content decays and loses citations.
Why it fails: New content starts with zero authority and takes months to build citations. Refreshing high-authority existing content often delivers 3-5x faster results.
The fix: Allocate 60-70% of content resources to strategic refreshes and 30-40% to new content. Existing assets are under-leveraged opportunities.
Mistake 7: Ignoring Competitive Dynamics
What it looks like: Refreshing in a vacuum without checking what competitors are doing or how AI platforms are citing in your space.
Why it fails: Citation share is relative. Even if your content improves, you lose ground if competitors are improving faster.
The fix: Start every refresh cycle with competitive analysis. Understand what's working for competitors and identify gaps you can exploit.
Conclusion: Make Content Refresh Your Competitive Advantage
The companies dominating AI search visibility in 2026 aren't the ones publishing the most new content. They're the ones systematically maintaining their existing content libraries with citation-focused refresh strategies.
Here's what separates winners from losers:
Losers:
Refresh randomly when traffic drops
Make superficial updates (date changes, minor tweaks)
Focus on traditional SEO metrics (rankings, backlinks)
Treat refresh as reactive cleanup work
Have no measurement framework for citation performance
Winners:
Refresh proactively on documented cadences before citations decay
Execute substantive improvements using structured frameworks
Optimize for citations first, rankings second
Treat refresh as strategic revenue protection
Track citation share and tie results to business outcomes
The framework in this guide moves you firmly into the winner category. You now have:
What to update: The 7-layer refresh checklist that ensures every element AI platforms evaluate gets systematically improved
When to refresh: Tiered cadences based on content type, competitive dynamics, and business value
How to execute: A step-by-step workflow with quality gates that prevent superficial updates
Your Next Steps
Week 1: Audit and prioritize
Export your content inventory
Categorize every page into Tiers 1-4
Track current citation performance for Tier 1 content
Identify your top 10 refresh opportunities using the Priority Score model
Week 2: Build your framework
Customize the 7-layer checklist for your content types
Set refresh cadences for each tier
Assign ownership (who's responsible for Tier 1 vs Tier 2?)
Set up basic citation tracking (even if manual initially)
Week 3-4: Execute your first refresh cycle
Start with your #1 priority page (highest Priority Score)
Work through Layers 1-7 systematically
Document time invested and challenges encountered
Publish and promote the refresh
Week 5-12: Measure and iterate
Track citation performance weekly
Monitor traditional SEO metrics monthly
Document what worked and what didn't
Use learnings to refine your next refresh cycle
The Compounding Effect
Here's the real power of systematic content refresh: It compounds.
Each refresh cycle you complete:
Improves citation rates, driving more brand awareness
Protects and grows revenue from existing high-value pages
Builds team expertise in citation-first optimization
Generates data to refine your framework
Creates defensible competitive moats as rivals chase new content
After 3-4 cycles (roughly 12 months), your content library becomes a self-reinforcing advantage. You're not fighting citation decay, you're proactively maintaining category leadership through disciplined execution.
Get Expert Help
If you want specialists to help implement this framework from auditing your content library and building custom refresh cadences to executing high-stakes Tier 1 refreshes Passionfruit's AI SEO team specializes in citation-first optimization strategies.
We've helped clients recover citation share, increase AI referral traffic by 200%+, and attribute millions in revenue to improved AI visibility. Book a free consultation to see how a structured refresh program could work for your content library.
Related Resources
Want to dive deeper into AI search optimization? These guides complement the refresh framework:
Generative Engine Optimization: Complete Framework for AI Search - Understand the broader GEO strategy that refresh supports
How to 10x Your Brand Mentions in AI Search Results - Deep dive on citation optimization tactics
Google's Guidance on AI-Generated Content - Official position on content quality in the AI era
Ready to stop losing citations to competitors? Download our free Content Refresh Checklist by starting a free trial and start protecting your AI search visibility today.
FAQs
How often should I refresh content for AI search vs traditional search?
Traditional SEO operated on 6-12 month refresh cycles for most content. AI search demands faster cadences:
Tier 1 content: Full refresh every 90 days, freshness updates monthly
Tier 2 content: Full refresh every 6 months, freshness updates quarterly
Tier 3 content: Annually or as needed
The difference stems from AI platforms' preference for recency. Pages not updated in 90+ days see citation rates drop 40-60% even when information remains accurate. That said, frequency matters less than quality of updates. A substantive quarterly refresh beats superficial monthly updates.
Can I automate content refreshes with AI writing tools?
Partially. AI writing tools can help with specific layers:
Good automation candidates:
Updating statistics (AI can find current data)
Rewriting examples with more recent alternatives
Generating FAQ questions based on related queries
Creating initial drafts of new sections to address gaps
Poor automation candidates:
Structural improvements (AI often makes hierarchy worse)
Evidence verification (AI can hallucinate sources)
Strategic decisions about what to update
Quality assessment of citation-worthiness
Use AI tools to accelerate research and drafting, but always apply human editorial review before publishing. Fully automated refreshes typically hurt citation rates because AI writing tools produce generic output that lacks the evidence and entity coverage AI platforms favor.
Should I change URLs when refreshing old content?
Almost never. Here's why:
Keep existing URLs when:
The core topic remains the same (95% of cases)
The page has backlinks you want to preserve
The URL already ranks well
Existing URLs have built-up authority and backlink profiles. Changing URLs forces you to rebuild that equity from scratch via 301 redirects, which always leak some authority.
Only change URLs when:
The topic has fundamentally shifted (rare)
The old URL is poorly structured and actively hurts SEO
You're consolidating multiple weak URLs into one strong one
If you must change, set up proper 301 redirects and update all internal links.
What's the ROI of systematic content refresh vs creating new content?
Refreshes typically deliver 3-5x better ROI than new content for these reasons:
Refresh advantages:
Existing pages already have domain authority and backlinks
Changes can impact rankings/citations within weeks vs months
Less resource-intensive (2-4 hours vs 8-12 hours for new content)
Compounds existing investment rather than starting from zero
New content advantages:
Captures entirely new keywords and topics
Expands total topical coverage
Can target emerging opportunities competitors haven't addressed
Optimal strategy: 60-70% of content resources on strategic refreshes, 30-40% on new content. This balances leverage (refresh) with expansion (new).
How do I know if my refresh actually improved citation rates?
Track these indicators 4-8 weeks post-refresh:
Primary signals:
Increased citation frequency when querying target keywords
Higher citation share vs competitors
More prominent citations (primary source vs brief mention)
Secondary signals:
Referral traffic increases from chatgpt.com, perplexity.ai
Brand search volume lift
Improved traditional rankings
Lagging signals:
Organic traffic increases
Conversion rate improvements
Revenue attribution
If you see improvements in primary/secondary signals but not lagging indicators, give it more time business metrics take 8-12 weeks to materialize.
If you see no movement in primary signals after 8 weeks, the refresh likely didn't address the real citation barriers. Review Layers 1-4 for gaps.
Do I need different refresh strategies for different AI platforms?
Yes, but the core framework applies universally. Platform-specific nuances:
ChatGPT:
Heavily weights recency (pages updated within 30-60 days)
Prefers structured, extractable content
Cites based on training data + real-time web access
Perplexity:
Extremely sensitive to freshness (pages from last 1-2 weeks)
Often cites news sources and recent updates
Real-time web retrieval means constant re-evaluation
Google AI Overviews:
Balances freshness with authority
Favors pages already ranking well in traditional results
Schema markup particularly important
Claude:
Moderate freshness preference
Strong emphasis on evidence and attribution
Detailed, comprehensive coverage performs well
The 7-layer framework addresses all these nuances. Adjust refresh frequency based on which platforms matter most to your audience, but layer priorities remain consistent.
Should I refresh content that's already getting good AI citations?
Yes, through maintenance refreshes. Here's why:
Even high-performing content faces competitive pressure. Competitors are constantly improving their content to capture citations you currently own. Proactive maintenance refreshes protect market share.
What if my team doesn't have bandwidth for systematic refreshes?
Prioritization is everything. You can't refresh everything, but you can protect your highest-value assets:
Minimum viable refresh program:
Focus exclusively on Tier 1 content (top 10-20 revenue-driving pages)
Refresh each quarterly using Layers 1-5 only
Skip Tier 2 and Tier 3 content entirely until you have more resources
How does content refresh interact with our existing content strategy?
Refresh should be integrated into your content strategy, not treated as separate:
Content calendar integration:
Block off 30-40% of content calendar for refresh work
Schedule refresh sprints quarterly for Tier 1 content
Treat refreshes like new content with briefs, deadlines, and quality gates
Topic cluster strategy:
Refresh pillar content first, then supporting cluster content
Ensure internal linking between refreshed pages reinforces topical authority
Use refresh opportunities to identify gaps in cluster coverage
Seasonal alignment:
Time refreshes around product launches, industry events, or seasonal trends
Refresh competitive comparison content before peak buying seasons
Update industry trend content at year-end/year-start transitions
New content decision:
Before creating new content, ask: "Could we refresh existing content to cover this?"
New content is justified when: (a) topic is truly net-new, (b) existing content can't be repositioned, or (c) we need to expand keyword coverage
Default to refresh unless new content clearly makes more sense
The best content strategies treat refresh as a first-class activity, not an afterthought when traffic drops.
Can I refresh content myself, or do I need specialized expertise?
It depends on complexity:
You can DIY if:
Content is Tier 2 or Tier 3 (lower stakes)
Updates are primarily Layer 5 (freshness) and Layer 7 (visuals)
You have clear competitive benchmarks to follow
Your team has strong editorial skills
Consider specialist help for:
Tier 1 revenue-critical content (high stakes, complex optimization)
Technical Layer 6 work (schema markup, semantic HTML)
Competitive spaces requiring strategic positioning
Comprehensive audits and prioritization across large content libraries
Most teams handle Tier 2-3 refreshes internally and bring in specialists for Tier 1 strategic content or technical optimization. This hybrid approach balances cost with quality.
If you need expert help, Passionfruit's AI SEO team can audit your content, build custom refresh frameworks, and execute high-value refreshes that prioritize citations and revenue over vanity metrics.